AI is the best and fast technology of the 21 century.From tone- driving buses to virtual sidekicks like Siri and Alexa, AI is reshaping diligence, revolutionizing diurnal life, and pushing the boundaries of what machines can achieve. But what exactly is AI, how is it created, and how does it serve?
What’s AI?
AI systems are designed to perform tasks that generally bear mortal intelligence, similar as feting patterns, making opinions, understanding language, and working complex problems. AI can be distributed into two primary types
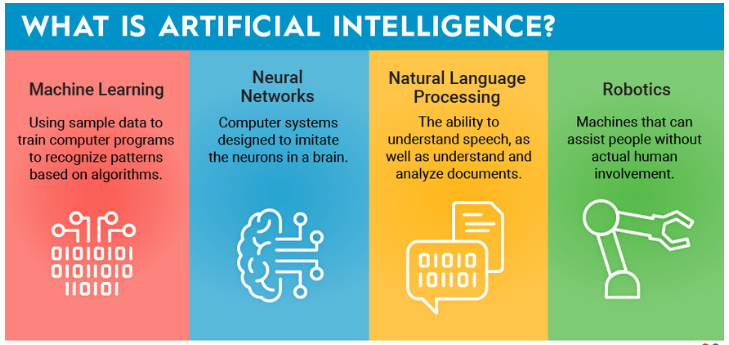
Narrow AI( Weak AI) These systems are designed to handle a specific task. exemplifications include recommendation algorithms on streaming platforms like Netflix, or voice sidekicks like Google Assistant. Narrow AI excels at one particular function but lacks the capability to perform outside of its designated task.
General AI( Strong AI) General AI aims to perform any intellectual task a human can do. This position of AI remains academic , as current technology has not reached the point where machines can authentically mimic mortal cognitive capacities across the board.
How is AI Made?
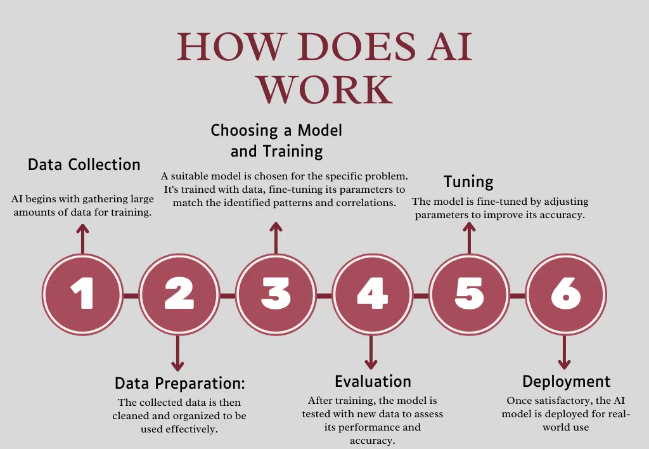
Creating AI involves several way that integrate mathematics, computer wisdom, data analysis, and engineering. Below are the crucial stages in erecting AI systems
Data Collection AI needs data to learn and make informed opinions. This data can come from colorful sources, including images, textbook, audio, vids, and stoner relations. High quality data is must for effective output. For illustration, to train a facial recognition AI, large datasets of mortal faces are needed.
This involves drawing the data, handling missing values, and transubstantiating it into a format suitable for machine literacy algorithms. point birth ways are used to punctuate important aspects of the data, perfecting the effectiveness of the model.
Choosing a Model The coming step is opting the applicable model to train the AI. Machine literacy models, like decision trees, neural networks, or support vector machines( SVMs), are chosen grounded on the problem the AI needs to break. Each model type has its strengths depending on the complexity and type of data.
Training the Model The model is also trained using the preprocessed data. This involves feeding the AI system exemplifications from the dataset, allowing it to identify patterns and make prognostications. During training, algorithms acclimate parameters and weights within the model to minimize crimes and ameliorate delicacy.
Testing and Evaluation After training, the AI is tested on a separate set of data that it has n’t seen ahead. This allows inventors to assess how well the AI performs in real- world situations. Common criteria for assessing AI include delicacy, perfection, recall, and F1 score.
Deployment and conservation Once the AI passes testing, it’s stationed into product where it interacts with druggies. nonstop monitoring is necessary to insure it performs well, and updates may be demanded as new data becomes available or the system’s terrain changes.
How AI Works
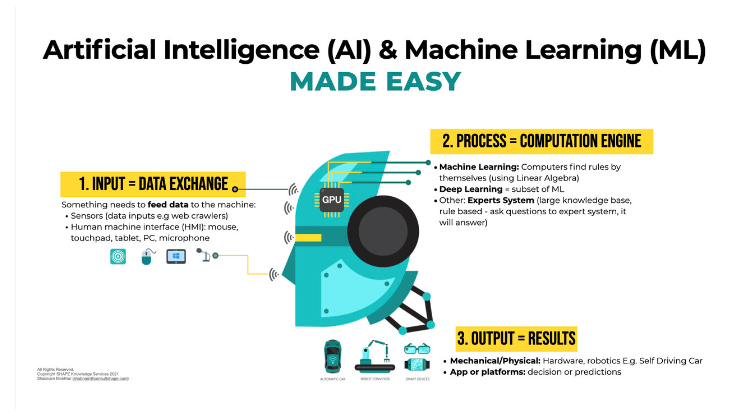
At the core of utmost AI systems is machine literacy( ML), a subset of AI that enables systems to learn from data and ameliorate over time without unequivocal programming. Then is how machine literacy and AI work together
Input Data The system receives input data in the form of textbook, images, sound, or other types. For case, in natural language processing( NLP), input data could be rulings in a language, while in computer vision, it could be images.
literacy Process The AI model processes the input using complex fine algorithms. For machine literacy, this involves chancing patterns in data. In deep literacy, which is a subfield of ML, neural networks are used to perform tasks like image recognition or language restatement.
Making prognostications Once trained, the AI model can make prognostications or opinions grounded on new input data. For illustration, a trained AI chatbot can give accurate responses to client inquiries by assaying the input textbook and matching it to known patterns.
Feedback Loop AI systems frequently have a feedback circle where they ameliorate over time. As they reuse further data or admit stoner input, they acclimate their algorithms to come more accurate and effective.
Decision- Making AI can also perform logic and decision- timber. In recommendation systems like those used by Amazon or Spotify, AI determines what products or music to suggest grounded on once stoner geste .
Advantages of AI
Automation of Repetitive Tasks: AI can automate routine tasks, increasing efficiency and allowing humans to focus on more complex activities.
Enhanced Decision-Making: AI analyzes vast amounts of data quickly, helping organizations make better data-driven decisions.
Increased Productivity: AI systems perform tasks faster and with greater accuracy than humans, boosting overall productivity in various industries.
24/7 Availability: AI systems can work continuously without needing breaks, offering round-the-clock service in areas like customer support and security.
Reduction of Human Error: AI operates with high precision, reducing the likelihood of mistakes, especially in critical fields like healthcare and finance.
Disadvantages of AI
High Costs: Developing, implementing, and maintaining AI technology can be expensive, particularly for smaller businesses.
Job Displacement: As AI automates tasks, it may lead to the displacement of jobs, particularly in industries that rely on repetitive work.
Lack of Creativity and Emotional Intelligence: AI lacks human creativity and emotional understanding, limiting its ability to innovate or engage with complex human emotions.
Data Dependency: AI systems rely heavily on large datasets, and poor-quality or biased data can lead to inaccurate or discriminatory outcomes.
Privacy and Security Risks: The collection and use of vast amounts of personal data by AI raise significant privacy concerns, increasing the risk of data breaches and misuse.
Conclusion
AI is a rapidly evolving field with enormous potential. From enhancing productivity in businesses to transforming healthcare, AI is poised to impact virtually every industry. Understanding how AI is made, from data collection to model training, provides insight into its capabilities and limitations. As AI continues to advance, the question is no longer whether AI will shape the future, but how we can harness its potential responsibly.
